Protein Structure Prediction¶
Protein structure prediction is the task of predicting the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence. As structure determines function, protein structure prediction is of fundamental importance in biology and medicine. Here we support two state-of-the-art protein structure prediction methods: AlphaFold2-Multimer v3 and Protenix.
Features¶
-
All-atom structure modeling: On GeoBiologics, you can predict the atomic structure of almost all biomolecules, including proteins, RNA, DNA, small molecules, and their complexes.
-
Batch prediction: Supports batch prediction and Amber relaxation (optionally) of multiple sequences in the cloud.
-
Graphical interface: No need to configure the environment or use the command line; simply click on the graphical interface to complete the structure prediction.
Protenix¶
Inputs¶
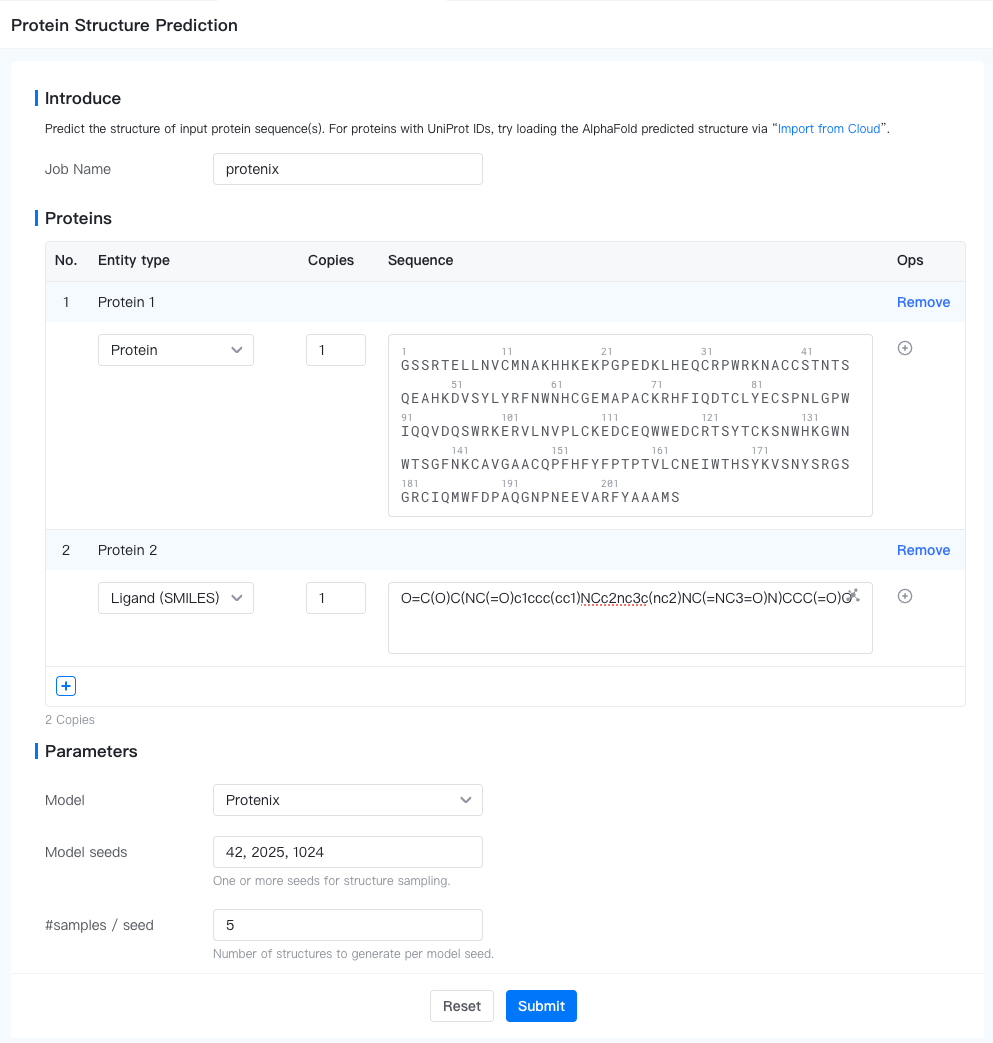
To submit a Protein Structure Prediction job, open the Project Editor and click "New Job" button on the left sidebar. Then click "Protein Structure Prediction" under the "Structure Modeling" group to open the job submission page.
-
Biomolecules: Describe your biomolecules. Note that you may predict multiple biomolecules in one job. Each biomolecule is predicted independently.
: Add a new biomolecule to the input.
- Biomolecule Name: Name of the biomolecule. Defaults to "Protein {i}" for the i-th biomolecule. To change it, hover above the biomolecule name, and click on the "
" button.
- Entity Type: Type of the entity within the biomolecule. Valid choices are "Protein", "RNA", "DNA", "Ligand (SMILES)".
- Copies: Number of copies of the current entity. Defaults to 1.
- Sequence: Sequence of the current entity. Different entity types have different sequence formats:
- Protein: Enter the amino acid sequence here with modifications as CCD code in parentheses, e.g. (ACE)GQLEEIAKQLEEIAWQLEEIAQG(NH2).
- RNA/DNA: Enter the nucleotide sequence here with modifications as CCD code in parentheses, e.g. GCGAGUAAU(8OG)UUAC.
- Ligand (SMILES): Enter a valid SMILES string, e.g. CCCC(C=O)O.
- Add Entity: Click the "
" button to add a new entity to the biomolecule. You can add up to 6 entities to a biomolecule.
Parameters¶
- Model seeds: A comma-separated list of seeds for structure sampling. More seeds results in higher likelihood of sampling high-quality structures in the expense of more compute.
- #samples/seed: Number of samples to generate for each seed.
Results¶
Click the job name in the Files & Jobs panel to view the job results.
The result summary is stored in a CSV file, which can be downloaded by clicking the "" button to the top-right of the Summary Table.
The summary table contains the following columns:
- name: Name of the biomolecule, as in input.
- seed: Seed used for structure sampling.
- sample: Sample index for the current biomolecule and seed.
- ranking_score: Model's ranking score for the current sample. Higher is better.
- gpDE: Global predicted Distance Error for the current sample. Lower is better.
In the rightmost column, you could click on the "" button to view the predicted structure.
AlphaFold2-Multimer v3¶
Inputs¶
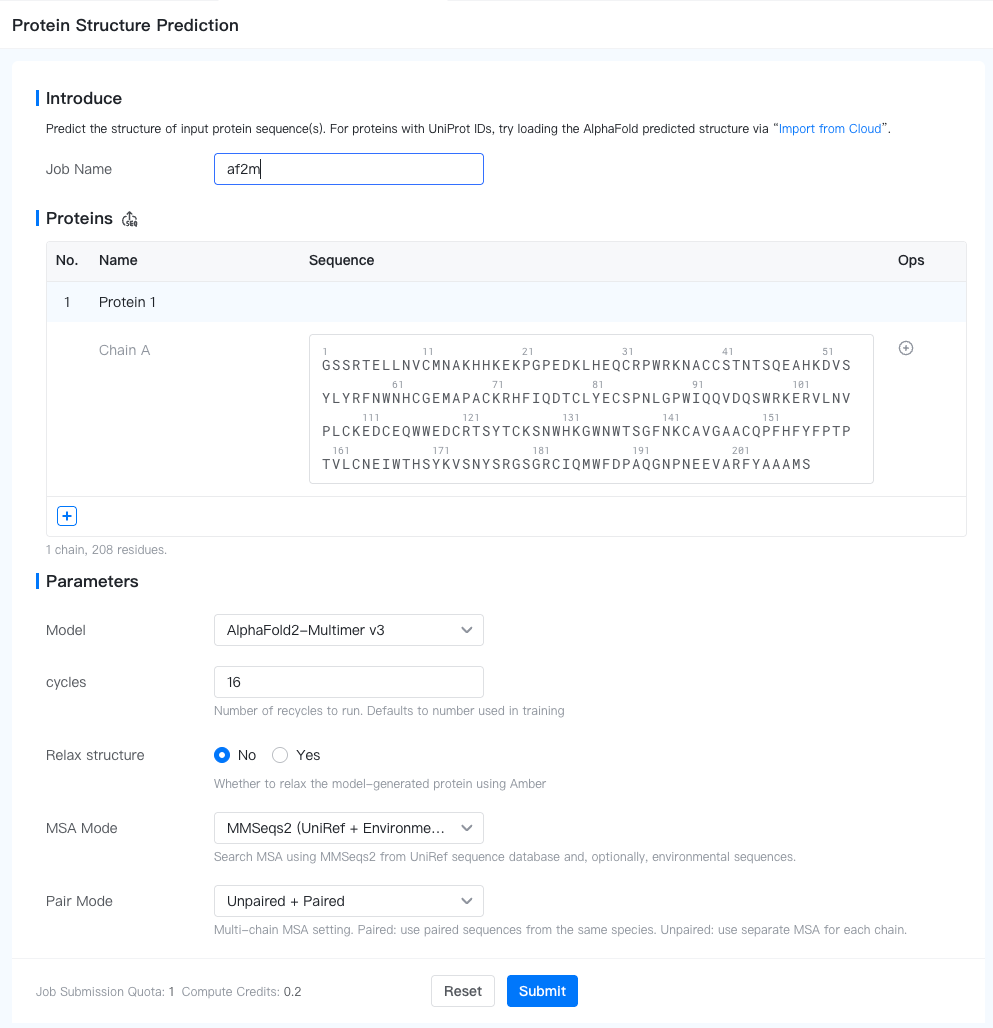
To submit a Protein Structure Prediction job, open the Project Editor and click "New Job" button on the left sidebar. Then click "Protein Structure Prediction" under the "Structure Modeling" group to open the job submission page.
-
Proteins: Input protein sequences in FASTA format. You can either enter the sequences in the input box or upload a FASTA file (by clicking the "
" button). Each protein, potentially multi-chain, is predicted independently.
: Add a new protein sequence to the input.
- Protein Name: Name of the protein. Defaults to "Protein {i}" for the i-th sequence. To change it, hover above the protein name, and click on the "
" button.
- Add Chain: Click the "
" button to add a new chain to the protein. AF2-Multimer can predict the structure of multi-chain proteins. We recommend no more than 9 chains and 1000 residues in total.
-
Job Name: Name of the job. Note that the job name must be unique within the project.
Parameters¶
- # cycles: Number of recycles to run (1-48). Defaults to 16.
- Relax structure: Whether to relax the model-generated protein using Amber (default to false).
- MSA mode: Search MSA using MMSeqs2 from UniRef sequence database and, optionally, environmental sequences. Valid choices are "MMSeqs2 (UniRef + Environmental)" (Default), "MMSeqs2 (UniRef)", "Single sequence (No MSA)".
- Pair mode: Multi-chain MSA setting. Paired: use paired sequences from the same species. Unpaired: use separate MSA for each chain. Valid choices are "Unpaired", "Paired", "Unpaired + Paired" (Default).
Results¶
Click the job name in the Files & Jobs panel to view the job results.
The result summary is stored in a CSV file, which can be downloaded by clicking the "" button to the top-right of the Summary Table.
The summary table contains the following columns:
- name: FASTA label, as in input.
- sequence: FASTA sequence, as in input.
- plddt: Predicted lDDT (local Distance Difference Test) scores from five AF2 models for the generated protein. Higher is better. The per-residue lDDT scores are stored in the b-factor of the output .pdb files. You could view them by changing the color theme of the Cartoon representation (of the Polymer component) to "Atom Properties > Uncertainty/Disorder".
- ptm: Predicted TM (Template modeling) scores from five AF2 models for the generated protein. Higher is better.
In the rightmost column, you could click on the "" button to view the predicted structure.
If you enabled the "relax" option, you would find two files in the dropdown menu: one for the unrelaxed structure and one for the relaxed structure.